High-Resolution Vector-Borne Disease Risk Assessment
Goal
We wish to identify the risk of vector-borne diseases at the resolution of a neighborhood. This will enable effective and targeted public health interventions, such as integrated vector control measures.
Challenges
Human mobility plays a critical role in the spread of vector-borne diseases. Conventional data sources do not have the required spatial and temporal resolution. Furthermore, traditional models have difficulty accounting for demographic heterogeneity.
Approach
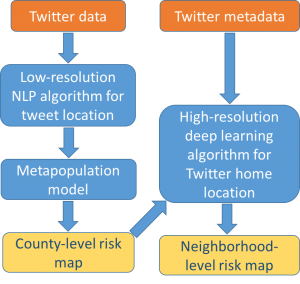
We use social media data to model human mobility. In particular, we use Twitter data to identify locations visited by people who have recently been to a disease-affected region.
- We first compute the flux of such persons into different counties using Natural Language Processing techniques on tweet content.
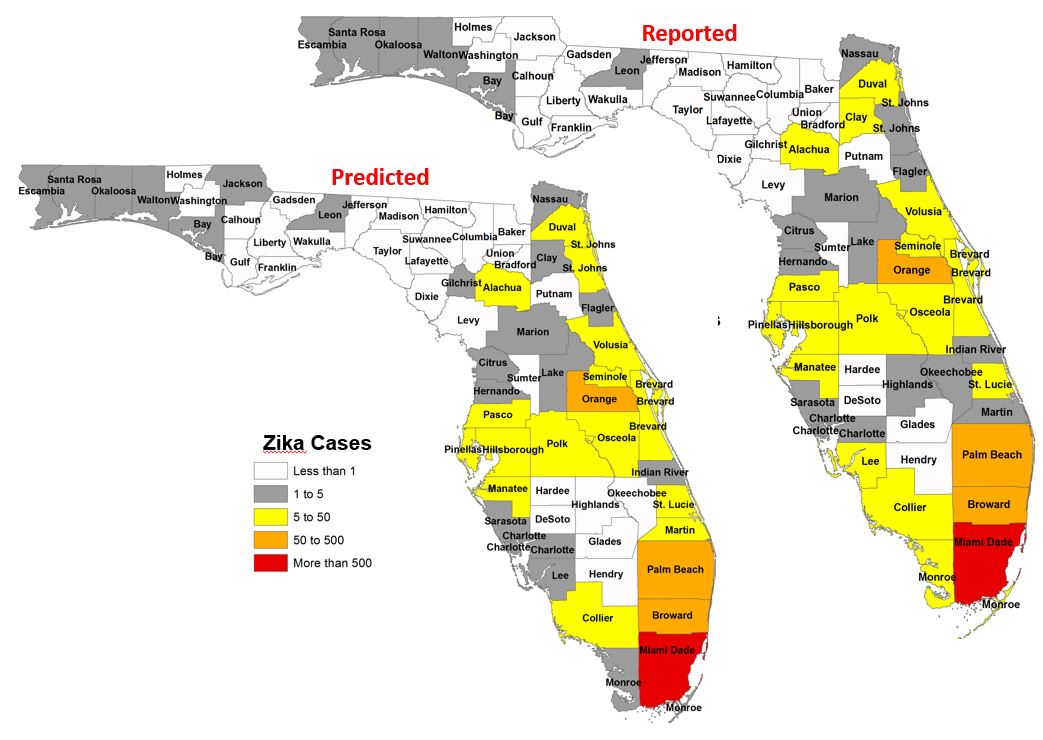
- We input this population flux into a meta-population model to identify counties at risk of disease importation.
- We then target high-risk counties for a fine-scale model. We leverage our novel deep learning workflow on Twitter metadata for determining home-locations of users to identify high-risk neighborhoods.
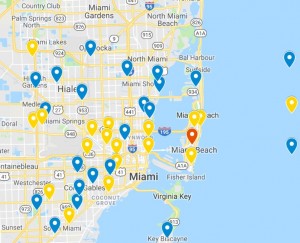
Results
| Predicted high-risk neighborhoods | Actual high-risk neighborhoods |
|---|---|
| Miami Beach | Miami Beach |
| Wynwood | Wynwood |
| Miami Airport | Little River |
